The proposed NIH budget cuts pose a serious risk to U.S. biomedical research, with rural states and underserved communities facing the harshest impact. These areas rely heavily on federal funding to sustain their research infrastructure and address unique public health challenges. The IDeA program, designed to support underfunded states, would suffer significant setbacks. Furthermore, reducing indirect cost reimbursements would weaken universities’ ability to maintain research facilities. As legal battles continue, preserving NIH funding is crucial to ensuring equitable healthcare advancements and economic growth across all states
NIH Funding Cuts: Impact on Rural States
Introduction
Recent proposals to cut the budget of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) pose a significant threat to U.S. biomedical research, public health, and the national economy. These potential reductions could hinder critical scientific progress that has long positioned the United States as a global leader in medical innovation. Beyond laboratories and research institutions, these cuts risk slowing the development of new treatments for devastating diseases, jeopardizing the future health of millions of Americans and weakening a sector that generates substantial economic benefits.
Disproportionate Impact on Rural States and Underserved Communities
While NIH budget cuts would affect the entire U.S. research landscape, their impact would be particularly devastating for rural states and underserved communities. These regions, already facing significant challenges in healthcare access and research resources, heavily rely on federal funding to maintain their scientific infrastructure and address their specific health issues.
Rural states, which generally have fewer institutional resources and a more limited private sector to offset federal funding losses, would see their research capacities significantly diminished. These areas, often grappling with unique public health challenges related to the environment, local industries, or limited access to care, risk losing the tools needed to develop solutions tailored to their specific needs.
The IDeA Program and Affected States
The NIH’s Institutional Development Award (IDeA) program was specifically designed to strengthen research capacities in states that traditionally receive less federal funding for biomedical science. This program targets 23 U.S. states and Puerto Rico, including:
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arkansas
- Delaware
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Mississippi
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Vermont
- West Virginia
- Puerto Rico
These states, primarily representing rural or low-population-density regions, have historically received a smaller share of NIH funding compared to established research hubs in states like California, New York, or Massachusetts. The IDeA program aims to correct this imbalance by strengthening local research infrastructure and developing scientific talent in these underrepresented areas.
Examples of Local Health Challenges
NIH funding plays a crucial role in addressing region-specific health issues, highlighting the importance of tailored support:
- In West Virginia and Kentucky, NIH-funded research has advanced the understanding of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, an occupational disease particularly affecting mining industry workers in these states. This work has led to improved early screening methods and the development of essential prevention strategies for mining communities.
- In Hawaii, NIH funding supports critical research on dengue and other tropical diseases that pose specific threats to this island region. These studies not only protect the local population but also provide valuable insights applicable to other tropical and subtropical areas of the U.S.
- In rural areas of North Dakota and South Dakota, NIH grants have enabled the development of innovative telemedicine programs that improve access to specialized care for geographically isolated populations, reducing health disparities.
Proposed Budget Cuts and the Indirect Costs Policy
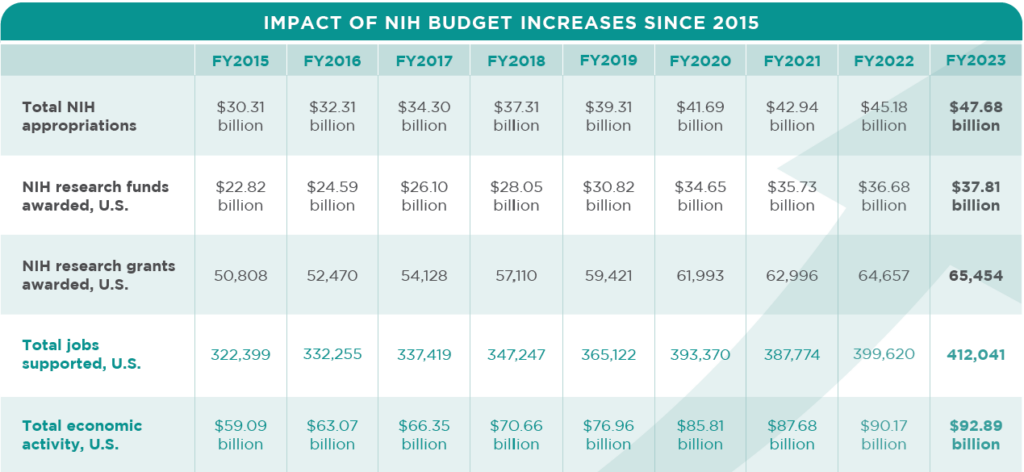
The Trump administration’s proposals include a drastic reduction in the NIH budget, estimated at $5.5 billion annually. This cut would represent approximately 18% of the agency’s total budget, significantly compromising its ability to fund new research projects and maintain existing programs.
Of particular concern is the proposal to cap indirect cost reimbursement rates at 15%, far below the current average rate of around 52% for universities. This measure, framed as a reform to reduce administrative expenses, actually threatens the fundamental operations of research infrastructure across the country.
Explanation of Direct and Indirect Costs
To understand the impact of this policy, it is essential to distinguish between the two types of costs associated with NIH-funded research:
- Direct costs are expenses directly attributable to a specific research project. They include:
- Salaries and benefits for researchers and lab staff
- Laboratory equipment and supplies
- Costs related to experiments and testing
- Travel directly linked to the project
- Indirect costs (or overhead) are expenses necessary to maintain the infrastructure that makes research possible but cannot be easily attributed to a specific project. They include:
- Maintenance and operation of research facilities
- Utilities (electricity, heating, water)
- Administrative and support services
- IT systems and networks
- Regulatory compliance and safety programs
- Libraries and information resources
These indirect costs are essential to the proper functioning of research institutions and represent real expenses that cannot simply be eliminated or ignored.
Impact of Reducing Indirect Costs
The proposed cap on indirect costs at 15% would have particularly severe consequences for IDeA states, which already have limited resources to maintain their research infrastructure.
For these institutions, such a reduction would mean:
- Inability to adequately maintain existing research facilities
- Challenges in complying with research safety and ethics regulations
- Reduced capacity to provide necessary administrative support to researchers
- Increased competitive disadvantage compared to larger, better-funded institutions in other states
Universities in rural states, which often have fewer options to offset these funding losses, would be forced to either absorb these costs (compromising other educational programs) or significantly reduce their research activities. In either case, the result would be a substantial weakening of biomedical research capacity in these already disadvantaged regions.
Consequences of NIH Funding Cuts
The proposed NIH funding reductions would have profound and far-reaching consequences:
- Slowed biomedical research and medical discoveries: Fewer research grants would slow the pace of scientific breakthroughs, delaying the development of new treatments and diagnostics.
- Job losses in research labs and related industries: The biomedical research sector directly employs hundreds of thousands of Americans and indirectly supports many more jobs. Funding cuts would lead to layoffs in labs and companies supplying research equipment and services.
- Disproportionate impact on rural and underserved states: IDeA states, which heavily rely on federal funding to maintain their research infrastructure, would see their ability to participate in biomedical innovation significantly reduced, widening the gap between established research hubs and less-developed regions.
- Delays in developing new treatments: Research on diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and heart disease would be hindered, delaying innovative therapies for millions of patients.
- Threats to diversity studies and healthcare for all populations: Research targeting the health issues of rural, minority, or disadvantaged populations would be particularly vulnerable to budget cuts, exacerbating existing health disparities.
For rural states, these consequences would be amplified by their reliance on federal funding and limited resources to offset these losses. Research institutions in these regions might be forced to significantly scale back their activities, depriving their communities of the economic and health benefits of biomedical research.
Temporary Block and Future Outlook
In response to these proposed budget cuts, a court injunction has temporarily halted their implementation, providing a reprieve for research institutions across the country. This judicial decision acknowledges the concerns raised by the scientific community regarding the potentially devastating impact of these funding reductions.
However, the future remains uncertain as the legal battle continues and budgetary pressures persist. Advocates for biomedical research, including bipartisan lawmakers, have emphasized the strategic importance of the NIH for public health and the U.S. economy, arguing for maintaining or even increasing its funding.
Importance of NIH Funding Access for All States
This controversy underscores the fundamental importance of equitable access to biomedical research funding for all U.S. states. The IDeA program has demonstrated that with proper support, institutions in traditionally underfunded states can make significant contributions to scientific advancements while addressing region-specific health challenges.
Maintaining and strengthening this support is essential for:
- Developing a diverse and geographically distributed scientific workforce
- Ensuring biomedical research addresses the needs of all U.S. populations
- Reducing health disparities between different regions of the country
- Stimulating economic development in rural states through research-related benefits
The proposed NIH budget cuts represent a significant threat to U.S. biomedical research, with particularly severe consequences for rural states and underserved communities. By reducing research funding and limiting indirect cost reimbursements, these measures risk hindering scientific progress, compromising research infrastructure, and exacerbating existing health disparities.
For IDeA states, which heavily depend on federal support to maintain their research capabilities, these cuts could undo years of progress in developing their scientific infrastructure and addressing region-specific health challenges.
In light of these challenges, it is crucial to recognize the value of the NIH not only as a driver of medical innovation but also as a tool for equity, enabling all U.S. states to participate in scientific advancement and reap its benefits. Preserving and strengthening this funding is an essential investment in the nation’s future health and the economic vitality of all its regions, particularly the most vulnerable.
IH funding cuts will hit red states, rural areas and …
NIH Funding Cuts Put Innovation, Health Equity, and Lives at Risk
NIH research cuts threaten the search for life-saving cures …
www.usnews.com › news › health-newsQ&A: NIH Funding Reduction Could Have ‘Devastating Impact’